Fork-Join框架:
- 是一个用于并行执行任务的框架,是一个将大任务分解成多个子任务,并且组合多个子任务的结果来获得大任务的答案的框架。
- Fork 就是把一个大任务切分为若干个子任务并行的执行,Join就是合并这些任务的执行结果,最后得到这个大任务的结果
- 主要用于完成计算密集型任务。使用了一种有效地智能方法来平衡可用线程的工作负载,这种方法称为工作密取(work stealing)
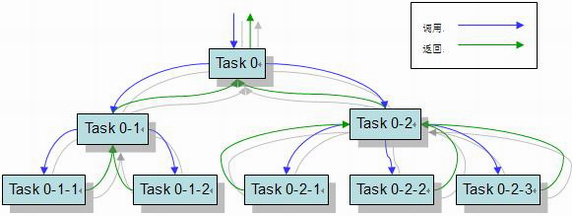
图 1 —— Fork-Join 模式示意图
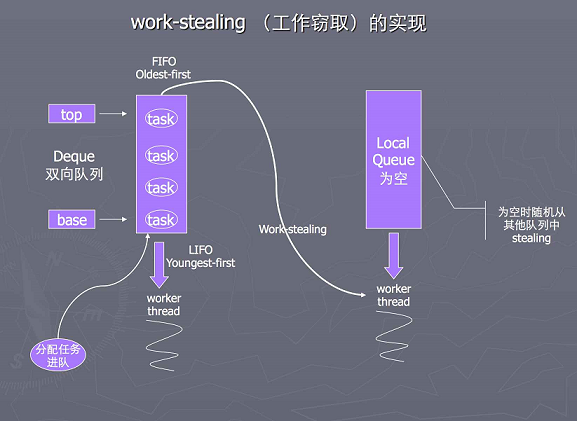
图 2 —— 工作密取示意图
RecursiveAction是ForkJoinTask的一个子类,代表了一类最简单的 ForkJoinTask:
例子:
1 class Counter extends RecursiveTask{ 2 //. . . 3 protected Integer compute() { 4 if (to - from < THRESHOLD) { 5 //solve problem directly 6 } else { 7 int mid = (from + to) / 2; 8 Counter first = new Counter(values, from, mid, filter); 9 Counter second = new Counter(values, mid, to, filter); 10 invokeAll(first, second); return first.join() + second.join(); 11 } 12 } 13 }
具体程序:
1 package forkJoin; 2 import java.util.concurrent.*; 3 /** 4 * This program demonstrates the fork-join framework. 5 * @version 1.00 2012-05-20 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class ForkJoinTest { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 final int SIZE = 10000000; 11 double[] numbers = new double[SIZE]; 12 for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) 13 numbers[i] = Math.random(); 14 Counter counter = new Counter(numbers, 0, numbers.length, 15 new Filter() { 16 public boolean accept(double x) { return x > 0.5; } 17 }); 18 ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(); 19 pool.invoke(counter);20 System.out.println(counter.join()); 21 } 22 } 23 24 interface Filter { 25 boolean accept(double t); 26 } 27 28 class Counter extends RecursiveTask { 29 public static final int THRESHOLD = 1000; 30 private double[] values; 31 private int from; 32 private int to; 33 private Filter filter;34 35 public Counter(double[] values, int from, int to, Filter filter) { 36 this.values = values; 37 this.from = from; 38 this.to = to; 39 this.filter = filter; 40 }41 42 protected Integer compute() { 43 if (to - from < THRESHOLD) { 44 int count = 0; 45 for (int i = from; i < to; i++) { 46 if (filter.accept(values[i])) 47 count++; 48 } 49 return count; 50 } else { 51 int mid = (from + to) / 2; 52 Counter first = new Counter(values, from, mid, filter); 53 Counter second = new Counter(values, mid, to, filter); 54 invokeAll(first, second); 55 return first.join() + second.join(); 56 } 57 } 58 }